Match the following condition with its causes metabolic acidosis – Match the following condition with its causes: metabolic acidosis. This topic delves into the intricate world of metabolic acidosis, shedding light on its definition, causes, clinical manifestations, management, and prevention. Brace yourself for an enlightening journey into the complexities of this condition.
Metabolic acidosis, a condition characterized by an abnormally low blood pH and high bicarbonate levels, arises from various underlying causes. Understanding these causes is paramount in devising effective treatment strategies and preventive measures.
Metabolic Acidosis Overview
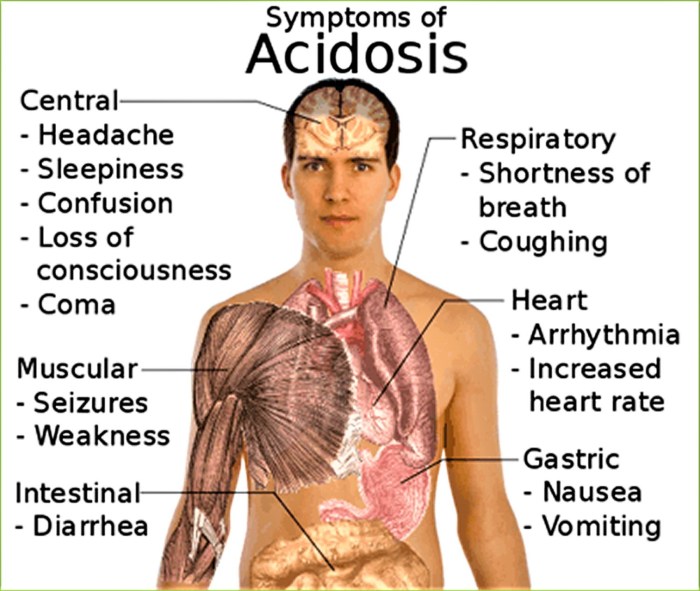
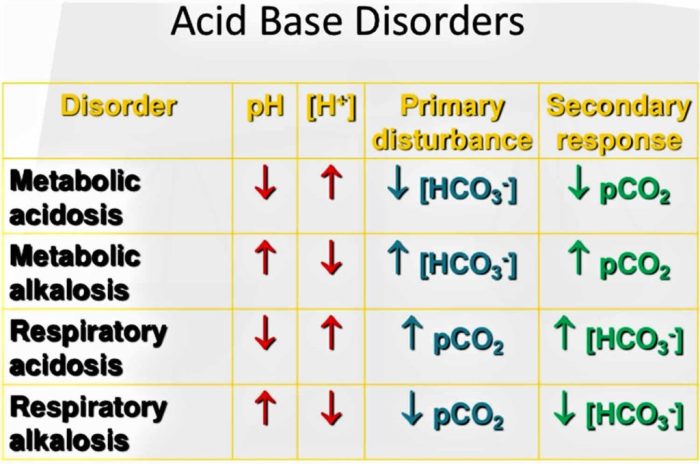
Metabolic acidosis is a condition characterized by an abnormally low blood pH (less than 7.35) and an increased bicarbonate concentration in the blood.
Causes of metabolic acidosis include:
- Increased production of acids, such as lactic acid or ketone bodies
- Decreased excretion of acids, such as in renal failure
- Loss of bicarbonate, such as in diarrhea or vomiting
The pathophysiology of metabolic acidosis involves the accumulation of acids in the body, which leads to a decrease in blood pH and an increase in bicarbonate concentration. This can result in a number of clinical manifestations, including:
- Kussmaul breathing
- Lethargy
- Confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
Causes of Metabolic Acidosis, Match the following condition with its causes metabolic acidosis
| Cause | Description | Examples | Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased production of acids | Production of acids, such as lactic acid or ketone bodies, exceeds the body’s ability to excrete them. |
|
|
| Decreased excretion of acids | Acids are not adequately excreted by the kidneys. |
|
|
| Loss of bicarbonate | Bicarbonate is lost from the body, such as in diarrhea or vomiting. |
|
|
User Queries: Match The Following Condition With Its Causes Metabolic Acidosis
What are the common causes of metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis can result from various causes, including diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal tubular acidosis, and ingestion of certain medications or toxins.
How is metabolic acidosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of metabolic acidosis involves measuring blood pH, bicarbonate levels, and anion gap. Additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause.
What are the potential complications of metabolic acidosis?
Untreated metabolic acidosis can lead to severe complications, including coma, seizures, and even death. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent these outcomes.