Natural selection – crash course biology #14 worksheet answers – Embark on a scientific expedition with our comprehensive answers to Crash Course Biology #14 worksheet on natural selection. This fundamental evolutionary concept unveils the intricate mechanisms that drive the survival and adaptation of species. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of nature’s relentless pursuit of the fittest.
Natural selection, as elucidated by Charles Darwin, stands as a cornerstone of modern biology. It explains how organisms with favorable traits have a higher probability of surviving and reproducing, passing on their advantageous genes to subsequent generations. This process gradually shapes the genetic makeup of populations, leading to remarkable adaptations and the diversity of life forms we witness today.
Natural Selection and Variation
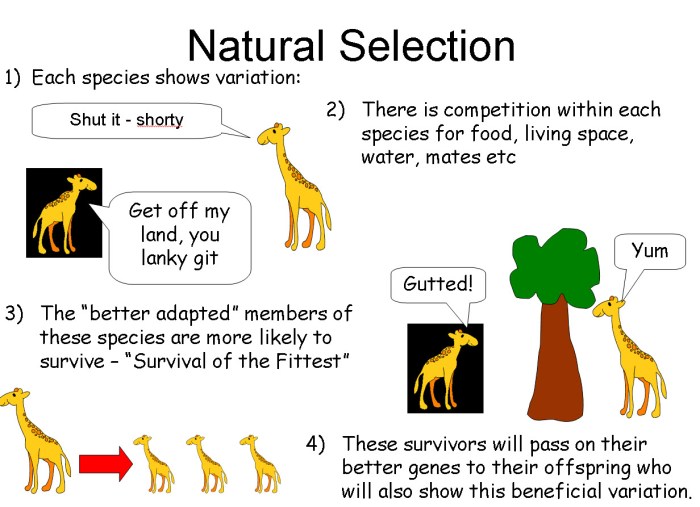
Natural selection is the driving force behind evolution, leading to the survival of individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment. It occurs when there is variation within a population, with some individuals possessing traits that give them an advantage in survival and reproduction.
These individuals pass on their advantageous traits to their offspring, gradually increasing the frequency of these traits within the population.
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is essential for natural selection to occur. It arises from mutations, genetic recombination during sexual reproduction, and other processes that introduce new genetic material into a population. This variation creates a pool of different traits, providing the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
Examples of Variation Affecting Fitness
- In a population of beetles, some individuals may have a darker coloration that provides camouflage in a dark forest, increasing their chances of avoiding predators.
- In a population of birds, some individuals may have longer wings that allow them to fly faster and escape predators or reach food sources more efficiently.
- In a population of bacteria, some individuals may have antibiotic resistance genes that provide an advantage in environments with antibiotics.
Mechanisms of Natural Selection
Overproduction, Competition, and Differential Survival
Natural selection relies on three key mechanisms: overproduction, competition, and differential survival. Overproduction occurs when a population produces more offspring than the environment can support. This leads to competition for resources such as food, water, and shelter. Differential survival refers to the fact that individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
Selective Pressure and Environmental Factors
Selective pressure refers to the environmental factors that favor certain traits over others. These factors can include predation, competition, availability of resources, and climate change. Selective pressure shapes the evolution of populations by favoring individuals with traits that increase their fitness in the current environment.
Types of Natural Selection: Natural Selection – Crash Course Biology #14 Worksheet Answers
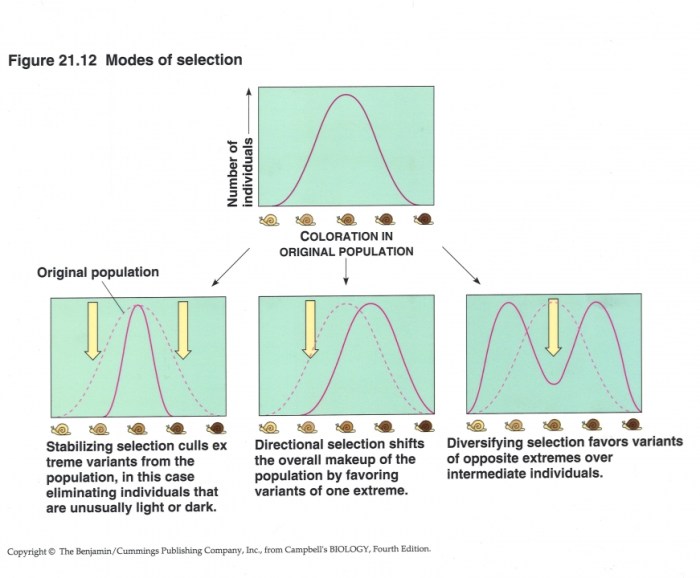
Directional, Stabilizing, and Disruptive Selection, Natural selection – crash course biology #14 worksheet answers
There are three main types of natural selection: directional, stabilizing, and disruptive.
- Directional selectionoccurs when one extreme of a trait is favored over the other. This leads to a shift in the average value of the trait over time.
- Stabilizing selectionoccurs when the average value of a trait is favored over both extremes. This maintains the stability of the trait within a population.
- Disruptive selectionoccurs when both extremes of a trait are favored over the average value. This can lead to the formation of two or more distinct groups within a population.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is a random process that can influence the evolution of small populations. It occurs when the frequency of alleles changes due to chance events, rather than natural selection. Genetic drift can lead to the loss of genetic variation and the fixation of alleles that may not be advantageous.
Evidence for Natural Selection
Fossil Evidence
Fossil evidence provides direct evidence of the changes in species over time. The fossil record shows a progression of forms, with transitional species connecting different groups of organisms. This supports the idea that species have evolved from common ancestors through natural selection.
Comparative Anatomy and Molecular Biology
Comparative anatomy and molecular biology provide evidence for common ancestry and evolution. Similarities in the anatomy and DNA of different organisms suggest that they share a common evolutionary history. Homologous structures, such as the forelimbs of vertebrates, provide evidence for the diversification of species from a common ancestor.
Artificial Selection
Artificial selection, the selective breeding of organisms by humans, provides a controlled experiment that demonstrates the principles of natural selection. By selectively breeding for desired traits, humans have created new breeds of animals and varieties of plants with specific characteristics.
Misconceptions about Natural Selection

Common Misconceptions
- Natural selection is a conscious process.Natural selection is a blind and automatic process driven by environmental pressures.
- Natural selection always leads to perfection.Natural selection favors traits that increase fitness in the current environment, but it does not necessarily lead to perfection.
- Natural selection is the only mechanism of evolution.Natural selection is one of several evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow.
Difference from Other Evolutionary Mechanisms
Natural selection differs from other evolutionary mechanisms in that it is a non-random process that favors traits that increase fitness. Genetic drift is a random process that can lead to changes in allele frequencies, while mutation introduces new genetic material into a population.
Expert Answers
What is the main mechanism of natural selection?
Natural selection operates through a combination of overproduction, competition, and differential survival. Organisms that possess traits that make them better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous genes to future generations.
Can natural selection lead to the development of new species?
While natural selection can drive significant changes in populations over time, it does not directly lead to the formation of new species. Speciation, the process of forming new and distinct species, typically involves the accumulation of genetic differences between populations that become reproductively isolated.
Is natural selection the only mechanism of evolution?
No, natural selection is not the only mechanism of evolution. Other mechanisms include genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation. However, natural selection is considered the primary driving force behind the adaptation of populations to their environments.